ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Background. The combination of various physical factors in the treatment of one nosology can elicit new integrative effects and enhance treatment efficacy. The study evaluates effectiveness of vibration-mechanical massage (VMМ) in patients with various nosological diseases. Methods of hardware VMМ have firmly entered the field of aesthetic medicine and cosmetology. The recent rapid development of VMМ technologies stimulates research and development work to study their effectiveness.
Objective: To evaluate the possibility of using VMМ in comprehensive postoperative rehabilitation programs.
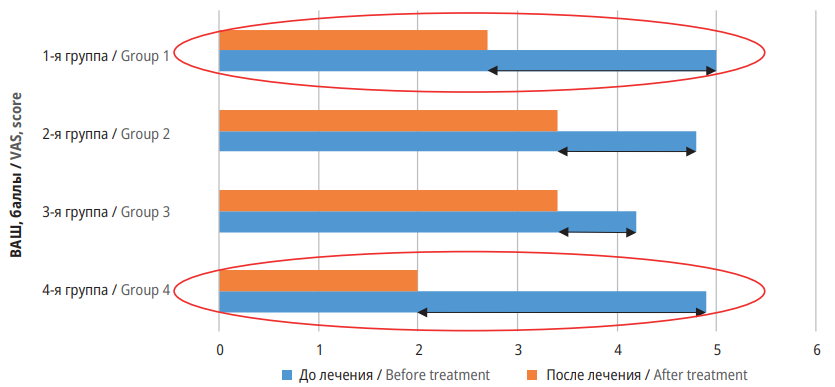
Material and methods. The Beautylizer Therapy massage device (Economic Electrical Solutions LLC, Russia) was selected for conducting VMМ procedures. The study involved 140 patients (67 (47.86%) men, 73 (52.14%) women) who had undergone different types of surgery. The participants were distributed into four groups of 35 individuals each. Group 1 included patients after operations on spinal structures; Group 2 – after mastectomy; Group 3 – after amputation of lower extremities; Group 4 – after stabilizing interventions on knee joints. All study groups were assessed using the visual analogue scale (VAS). To assess the functional status of patients within rehabilitation programs for different study groups, the following functional status questionnaires were used: for Group 1 – Scoliosis Research Society-22 (SRS-22) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI); for Group 2 – Short Form Medical Outcomes Study (SF-36); for Group 3 – Lequesne Algofunctional Index (LAI); for Group 4 – Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS).
Results. According to the VAS, a statistically significant reduction in pain syndrome was observed across all study groups, with the most pronounced effects noted in Groups 1 and 4. In Group 1, patients after correction for scoliotic deformity demonstrated a significant improvement in SRS-22 indicators “Back pain” and “Treatment satisfaction”. In this same group, patients after intervertebral disc surgery exhibited a mean ODI of 49.75% preoperatively (severe disability), which decreased to 36.25% postrehabilitation (moderate disability) (p<0.05). In Group 2, significant improvements were recorded in SF-36 “Physical Functioning”, “Role Physical Functioning”, and “Role Emotional Functioning”. Group 3 exhibited a marked decrease in pain intensity LAI value to the point of complete resolution (p<0.001). In Group 4, the most clinically significant differences in KOOS indicators were observed concerning pain and stiffness.
Conclusion. The data presented show that the VMM method, by targeting the myofascial components of musculoskeletal structures, is capable of alleviating nonspecific pain syndromes and may be recommended for clinical practice in various diseases and conditions.
Background. Magnesium deficiency (MD) is a prevalent issue among women after radical treatment for gynecological cancers, particularly in the context of surgical menopause. A lack of magnesium can significantly affect the quality of life of patients, causing various somatic and psychological disorders.
Objective: To assess the impact of a comprehensive “active” rehabilitation program on magnesium levels in women with vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) in surgical menopause.
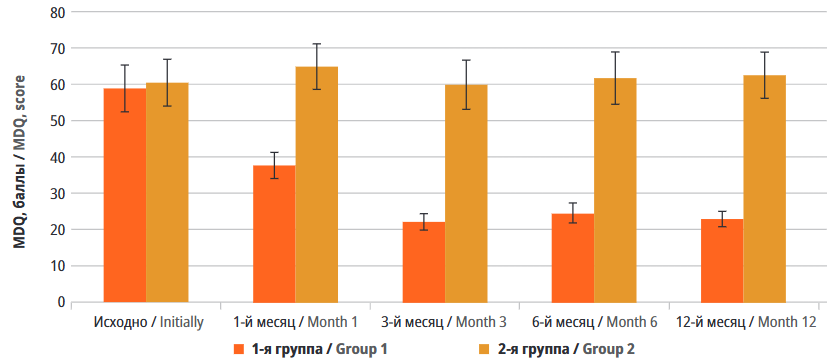
Material and methods. The study included 140 women with VVA after radical treatment for female genital cancer. Participants were divided into two groups: Group 1 (n=70) received comprehensive “active” rehabilitation, while Group 2 (n=70) underwent standard rehabilitation. MD manifestations were evaluated at Months 1, 3, 6, and 12 after surgery using the Magnesium Deficiency Questionnaire (MDQ) and the Magnesium Deficiency Assessment Test (MDAT). Additionally, laboratory tests were performed to measure blood magnesium levels.
Results. In the group receiving comprehensive “active” rehabilitation, a significant reduction in MD was observed as early as Month 1 (37.84±14.89 MDQ points compared to 65.10±26.30 points in the control group, p <0.01). By Month 3, symptoms of MD were nearly completely resolved (22.34±9.17 MDQ points). A similar trend was noted in MDAT results. Blood magnesium levels in Group 1 increased from 0.7±0.01 to 0.81±0.08 mmol/l at Month 1 and reached 0.90±0.06 mmol/l at Month 12. In contrast, the magnesium levels in Group 2 remained stable at 0.71–0.73 mmol/l throughout the study period.
Conclusion. The comprehensive “active” rehabilitation program demonstrated high efficacy in correcting MD in women with VVA undergoing surgical menopause, contributing to an improvement in their quality of life.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Background. Rehabilitation of athletes with identified neurological disorders is a challenging task for the rehabilitation team. The current system of patient management at the recovery stage cannot meet the needs of professional athletes. Therefore, a review of recent knowledge in this field with a view to determining future research directions represents a relevant task.
Objective: To identify the key specifics of providing rehabilitation assistance to professional athletes with neurological disorders.
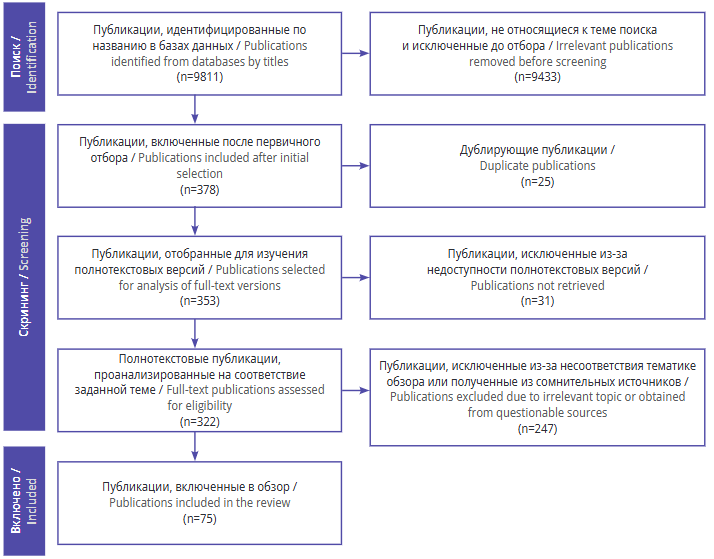
Material and methods. The search for publications was conducted using the following scientific databases and electronic libraries: PubMed/MEDINE, ScienceDirect, Cochrane Library, eLibrary, and CyberLeninka. A total of 9811 publications were retrieved, 75 of which fully met the selection criteria and were included in the review. The search and selection of sources was conducted taking the PRISMA recommendations into account.
Results. Rehabilitation of athletes with neurological disorders should be carried out with the participation of multidisciplinary rehabilitation team (MDRT), developing a personalized treatment strategy and monitoring its implementation. Particular emphasis should be placed on maximizing the impact on the patient’s body, while avoiding the occurrence of new complications and injuries. Maintaining continuity in providing rehabilitation support between departments and institutions is of importance in the process of restoring lost functions. Correction of neurological disorders requires a systematic approach and the use of both conventional and innovative rehabilitation methods.
Conclusion. Concerted efforts within MDRT and its high qualification ensure the most optimal outcome in the rehabilitation of athletes with neurological disorders. When managing such patients, early rehabilitation is of particular importance, especially among post-stroke patients. Physical load during exercise should be raised smoothly, high-intensity exercises are to be avoided.
Background. The quality of life of patients refers to important determinants in choosing an approach to disease treatment and rehabilitation strategy. However, certain clinical cases require limb amputation as the only effective method for alleviating life-threatening conditions, which necessitates medical rehabilitation for the patient.
Objactive: To summarize current approaches to rehabilitation for patients after limb amputation.
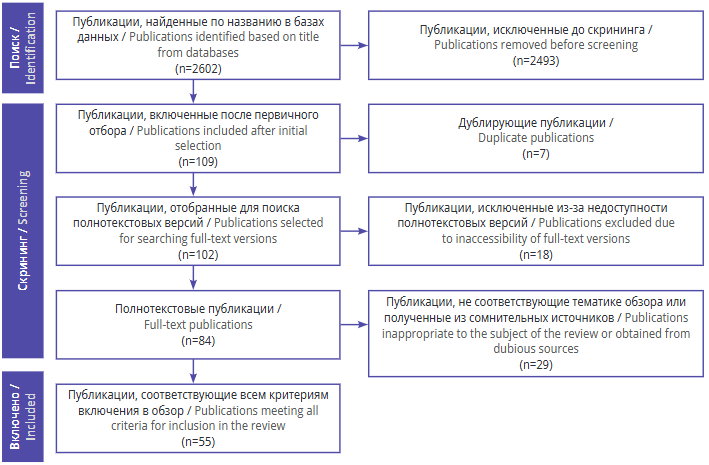
Material and methods. The search and screening were carried out in accordance with PRISMA recommendations. The study involved the following scientific databases: PubMed/MEDLINE, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, eLibrary, and CyberLeninka. Individual publications featured in the review were identified through search services. Among 2602 identified articles, 55 fully met the selection criteria.
Results. The studies highlight the significance of the chosen amputation technique in relation to the occurrence of complications and amount of tissue preserved. The decisions made at the stage of surgical treatment inevitably influence the selection of rehabilitation approaches and tools. Subsequently, the patient’s condition is assessed according to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health, identifying the key needs for nutritional support, medication management, and medical devices. A considerable focus in planning rehabilitation after limb amputation is placed on interventions aimed at reducing the incidence of complications and enabling full restoration of mobility, independence and social activity despite the defect. Rehabilitation of patients of this profile obtains a number of peculiarities depending on the amputated limb; however, multidisciplinary rehabilitation teams (MDRT) generally emphasize physical therapy, massage, prosthetics, physio therapy, medication and psychological support.
Conclusion. The analysis of current approaches to rehabilitation in patients who had undergone limb amputation demonstrated the importance of the rehabilitation and the necessity for a MDRT to determine the optimal strategy. Modern bionic prostheses are capable of nearly fully compensating for the loss of mobility and independence, regardless of the place of limb amputation, thereby achieving the stated objectives of medical rehabilitation. However, this efficiency is achieved after training in specialized prosthetic and orthopedic enterprises or medical institutions collaborating with these organizations.
Physiotherapy is a branch of practical medicine that investigates the effects of natural or artificially induced physical factors on human body used for patient treatment, medical rehabilitation, and disease prevention. A strong interest among medical professionals in physical treatment methods is attributed to their advantages over other therapeutic approaches, which include a significant expansion of the range of therapeutic interventions, shortened treatment durations, and enhanced efficacy of pharmacological agents. In recent years, a number of innovative techniques has significantly increased, thereby enabling medical care to be provided at a more advanced level. The global expansion of physiotherapeutic technologies is directly related to the balance between their availability, scientifically proven efficacy, and the impact of limiting factors. The presented literature review analyzes current trends in the development of physiotherapy, their practical significance and effectiveness, as well as highlights the key challenges hindering the successful implementation of rehabilitation techniques.
Regular evaluation of the effectiveness of the rehabilitation strategy as well as the individual methods applied is an integral element of modern personalized support. To obtain a denser flow of health information and assess compliance, the use of remote patient monitoring (RPM) in cardiovascular and neurological rehabilitation programs is appropriate. However, it is worth paying close attention not only to the obvious benefits of RPM, but also to the problems and challenges that may be an obstacle to widespread implementation of this system.
The search for the meaning of life is probably one of the most important questions a human asks himself through the whole lifetime. In times of social and economic upheaval, people often become deprived of understanding they had previously achieved, and sometimes they lose it through tragic experiences. Logotherapy is a method of restoring lost meanings, experiencing tragic events and using negative emotional feelings for a new impulse in life. The presented article analyzes the possibilities of applying logotherapy in the process of psychological rehabilitation based on the review of theoretical works and empirical studies. The key principles, techniques and approaches used in logotherapeutic practice are considered. Examples of using logotherapy are presented in various contexts, such as rehabilitation after traumatic events, addictions, job loss, serious illness, and bereavement.
Rehabilitation is recognized as a complex and comprehensive process that requires active involvement of the patients, their family members and various medical specialists. A successful recovery implies the coordinated efforts among all participants in the rehabilitation process, based on the latest scientific data and clinical experience. The presented article discusses an integrated approach to rehabilitation and emphasizes the significance of productive interaction between patients, their relatives, and multidisciplinary rehabilitation teams, which includes physicians from various fields, psychologists, social workers, and other professionals. This model of rehabilitation is aimed at achieving maximum restoration of patients' functions and quality of life.
ISSN 2949-5881 (Online)