ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Background. Gynecological cancers in women are a widespread type of oncology. Among them, endometrial cancer (EC) is often highlighted as one of the most common diseases in this group. The analysis of publications showed insufficient effectiveness of rehabilitation in patients with EC and recurrent atypical endometrial hyperplasia (rAEH).
Objective: to compare the state of patients with rAEH or EC after hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, depending on the recovery tactics.
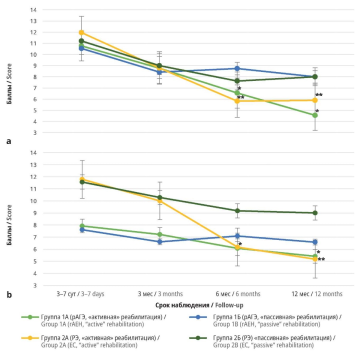
Material and methods. The study included 119 patients diagnosed with rAEH (n=58) or stage IA EC (n=61) after hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. The group of women with rAEH was divided into two subgroups: 1A (“active” rehabilitation, n=27) and 1B (“passive” rehabilitation, n=31); two subgroups were also formed from the cohort of EC patients: 2A (“active” rehabilitation, n=29) and 2B (“passive” rehabilitation, n=32). “Active’ rehabilitation included a comprehensive, personalized program, “passive” one was based on standard rehabilitation protocols. Apart from standard clinical examination of patients, their quality of life (QoL), physical condition as well as the levels of cytokines and other biochemical blood parameters were assessed.
Results. An analysis of the overall picture showed a high incidence of rAEH or EC in women aged 40–49 years. Comorbid pathologies, low QoL level and a number of significant changes in laboratory parameters were often observed. Regardless of the approach to rehabilitation, the patients' health improved over the course of 12 months. “Active” rehabilitation significantly improved psychological well-being, sexual function, overall QoL and a number of other objective health indicators of patients with rAEH or EC compared to standard rehabilitation course.
Conclusion. The overall picture of rAEH or EC patients was presented, the main factors that reduce QoL in women with these diseases were identified. A system of integral QoL assessment in patients with rAEH or stage IA EC was developed including subjective and objective parameters obtained during general clinical examination, laboratory tests and analysis of questionnairing results, which should be used to adequately monitor the state of patients after surgery and the effectiveness of rehabilitation. The advantage of comprehensive rehabilitation over standard protocols in terms of efficiency and speed of recovery was shown.
Background. In the 21st century, there is a clear trend towards an increase in the proportion of women with climacteric syndrome (CS) and surgical menopause. Medical care for such patients usually includes menopausal hormone therapy (MHT), which often causes changes in magnesium and pyridoxine metabolism and their deficiency, leading to the development of adverse reactions. Therefore, it is necessary to improve rehabilitation programs designed to increаse the quality of life (QoL) for this category of gynecological patients.
Objective: to assess the profile of women with CS and surgical menopause receiving and not receiving MHT and to identify the significance of magnesium deficiency (MD) effect on the recovery process.
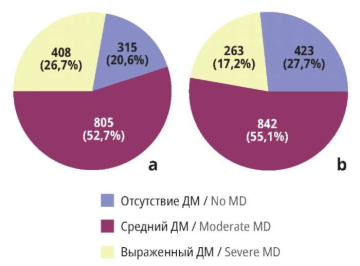
Material and methods. The observational non-interventional study included a total of 9168 women, of which 1528 patiеnts with CS and surgical menopause were taking MHT (Group 1), and 1528 patients with CS and surgical menopause were not taking MHT (Group 2). The Magnesium Deficiency Questionnaire (MDQ) was used to determine the number of participants with MD. A biochemical blood test was also performed, including determination of plasma magnesium concentration. The patients’ profile was analyzed for general somatic pathologies, obstetric and gynecological history, complaints, and MD symptoms using visual analogue scale. To assess QoL before the start of 4-week MD replenishing course and at the end of therapy, the World Health Organization Quality of Life Questionnaire (WHOQL-26) was applied.
Results. The MDQ data showed that the prevalence of DM in Group 1 was higher compared to Group 2. In both groups, women with hypomagnesemia had a higher incidence of viral infections, vegetative-vascular dystonia, osteochondrosis and arterial hypertension, more pronounced sleep disorders, irritability, back pain, rapid fatigue, and higher MDQ scores. After completion of the course of therapy with magnesium citrate and pyridoxine combination, the MDQ scores in patients with DM decreased along with an increase in plasma magnesium concentration. Besides, women's satisfaction with their physical, psychological, social wellbeing and microsocial support increased, and self-perception improved. A decrease in the severity of DM and a significant improvement in QoL according to WHOQOL-26 were demonstrated in patients with CS and surgical menopause after therapy.
Conclusion. The profile of patients with CS and surgical menopause, regardless of MHT, is often characterized by DM and decreased QoL. It seems reasonable to include blood magnesium level monitoring and DM correction in the comprehensive rehabilitation program for such patients.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Background. The problem of a significant reduction in the quality of life (QoL) of oncological patients remains relevant despite current achievements in medicine. The issue of standardizing methods for assessing QoL in such patients is relatively acute. Patients undergo this assessment from the diagnostic stage to the end of rehabilitation, so it’s important to choose an accurate and precise method for QoL evaluation.
Objective: to analyze existing questionnaire-based methods for assessing QoL in cancer patients.
Material and methods. The search for publications was conducted in the scientific databases PubMed/MEDLINE, ScienceDirect, and eLibrary. Additionally, the sources found by queries in Yandex and Google search engines by each researcher individually were considered. The review included 38 articles.
Results. The vast majority of questionnaires used to assess QoL in oncological patients can be divided into two large groups: based on QLQ-C30 and FACT-G. Despite the similarity between QLQ-C30 and FACT-G questionnaires, some shift in their focus was shown. QLQ-C30 is more oriented on physical indicators, and FACT-G is more aimed at social and emotional well-being. Besides them, questionnaires that proved to identify and monitor individual groups of symptoms and syndromes were presented: FSFI, HADS and Russian questionnaire on well-being, activity, mood.
Conclusion. The obtained results indicated a fairly wide choice of questionnaires for the overall assessment of QoL and its individual elements. They include both proven screening and monitoring tools and those requiring validation and expansion of the evidence base. Due to high effectiveness of questionnaires as QoL screening and monitoring tools, further work is needed to ensure that they are widely included in clinical guidelines.
Background. It is well known that the severe course of a new coronavirus infection (NCI) is often accompanied by a significant risk of hemostasis system disorders. Virus-associated coagulopathy in COVID-19 differs from its other types. Apparently, it is directly related to inflammatory processes and an inadequate response from the immune system.
Objective: to determine the main mechanisms of immune-mediated coagulopathy development in NCI patients and methods of correcting this pathological condition.
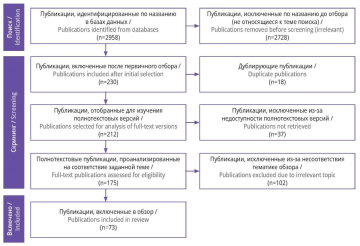
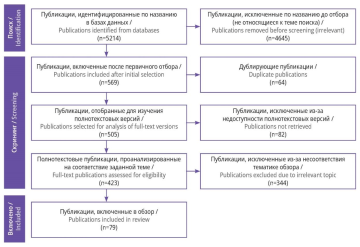
Material and methods. The search for studies devoted to the specifics of coagulopathy course in COVID-19, treatment and rehabilitation of patients with this complication was carried out in international scientific research databases PubMed/ MEDLINE, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect and scientific electronic library (eLibrary). The search depth was 20 years. The results of queries in search engines Yandex and Google were also taken. After selection of publications performed according to PRISMA recommendations, 73 articles were included in the review.
Results. A “vicious circle” associated with cytokine storm underlies the pathogenetic mechanisms of immune-mediated thrombosis in COVID-19 patients. A significant role of endothelial dysfunction, extracellular neutrophil traps (NETs), thrombocytopathy and changes in complement system activity is assigned to coagulopathy development. The therapy of this complication is aimed primarily at pathogenetic process. The effectiveness of anticoagulants, anti-inflammatory drugs, antiplatelet agents, drugs aimed at limiting the role of NETs and complement system in thrombosis development was shown. The expediency of preventive use of anticoagulants in COVID-19 patients was considered. Information was provided on the rehabilitation of NCI patients with coagulopathy. The effectiveness of combined anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant therapy in COVID-19 as a component of complex rehabilitation was indicated.
Conslusion. Inflammatory processes and immune response play an crucial role in coagulopathy development in NCI patients. The combination of all pathogenetic changes on the part of immune system, inflammatory response and hemostasis system makes it difficult to carry out therapeutic measures. The general scheme of rehabilitation for COVID-19 patients should include three stages, and timely use of combined anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant therapy is also advisable.
Background. Genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM) is characterized by a number of pathological changes, in particular urological disorders, vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) and sexual dysfunction. They are commonly accompanied by decreased quality of life (QoL) and often require medical intervention. At the same time, the steps taken to effectively solve this problem are not enough. Thus, it seems relevant to search for rehabilitation methods for VVA patients.
Objective: to determine the effectiveness of current rehabilitation methods for VVA patients.
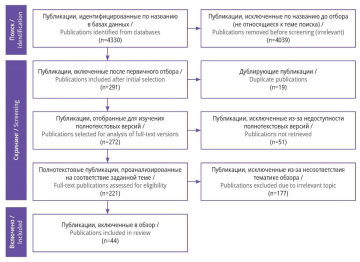
Material and methods. The search of publications in international scientific databases PubMed/MEDLINE, ScienceDirect, search engines and eLibrary revealed 4,330 publications, of them 44 sources were selected for the analysis after the screening procedure according to PRISMA scheme.
Results. VVA is based on decreased serum estrogen level and estrogen receptors quantity. Estrogen is a vasoactive hormone that promotes blood supply to the genitals and is involved in maintaining the normal genitourinary microflora. This may occur in women for age-related reasons or as a result of ongoing therapy or radical surgical intervention. At the same time, GSM is often formed, where VVA is one of the key elements. These changes are accompanied by sexual dysfunction, distress and decreased overall QoL in women. It is advisable to carry out complex personalized rehabilitation and QoL monitoring for such patients. The effectiveness of estrogen-containing therapy for topical use as well as adjunctive therapy with non-hormonal lubricants and moisturizing gels or creams was shown for VVA patients.
Conclusion. It was determined that VVA symptoms, in general, significantly affect the patients’ QoL, regardless of age. The necessity of developing specialized rehabilitation programs conducted by specialists of various profiles was noted. The effectiveness of these programs will be higher with timely diagnosis, which also requires significant attention.
Background. Epigenetics is a branch of genetics that studies the influence of external factors on gene expression. Many studies have shown the role of epigenetic regulation mechanisms in gene expression, including patients with cancer. Despite the clear prospects of using the principles and methods of epigenetics in the diagnosis, treatment and recovery, the implementation of this new technology remains at a relatively low level.
Objective: to determine the importance of epigenetic mechanisms in the diagnosis, outcome prognosis and rehabilitation of patients with oncological diseases.
Material and methods. The search for publications was performed in scientific databases and electronic libraries: PubMed/ MEDLINE, ScienceDirect, Google Schoolar, eLibrary. The review included 79 articles on the role of epigenetic mechanisms in the diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of cancer patients.
Results. DNA methylation, covalent histone modifications, and microRNA regulation are the most studied epigenetic changes (EGC) in cancer patients. Liquid biopsy is alternative approach to the detection of epigenetic biomarkers. A number of biomarkers were identified that make it possible to diagnose oncological diseases, e.g. lung cancer and breast cancer, and predict their course. Some EGC were assosiated with the implementation of rehabilitation measures, such as nutritional support, physical activity, maintaining circadian rhythms and acupuncture.
Conslusion. The analysis of publications confirmed the significant importance of EGC on the development of malignant neoplasms. The results indicated a sufficient number of studies dedicated to EGC biomarkers as new diagnostic tools and predicting the oncological disease outcome. But there is an insufficient number of studies on EGC mechanisms in rehabilitation. Further investigation on epigenetic mechanisms of variability will allow making significant progress in the development of targeted drugs and personalized rehabilitation of patients with malignant neoplasms.
Backround. Current medicine pays significant attention to an integrated approach in managing cancer patients, from the stage of diagnosis to rehabilitation. Sections on rehabilitation have been added to respective guidelines to maintain the proper quality of life of patients and standardization of clinical protocols. Due to the different levels of medicine in Europe, Russia and USA, it is important to analyze guidelines for supporting oncological patients at the rehabilitation stage.
Objective: to conduct a comparative analysis of guidelines for managing cancer patients.
Material and methods. The search and selection of publications were performed according to PRISMA recommendations. In scientific databases PubMed/MEDLINE, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, eLibrary as well as via search engines and the Rubricator of Clinical Guidelines of the Ministry of Health of Russia, 725 sources were found. After the selection procedure, 30 publications and guidelines were included in the review.
Results. Rehabilitation programs are presented in many Russian, American and European guidelines for the support of cancer patients. In Russian guidelines for managing patients with renal parenchyma and bladder cancer, a significant emphasis is made on the pre-rehabilitation and using fast-track approach. A lot of attention is paid to therapeutic physical culture and instrumental methods. American and European guidelines are more detailed, in particular, protocols for the correction of certain adverse events are presented, psychological assistance and complex rehabilitation play an essential role. The absence of specialized rehabilitation program in Russian clinical guidelines for supporting oncogynecological patients, and universal character of protocols were noted. According to foreign guidelines, the rehabilitation of such patients is multidisciplinary and personalized, and is carried out in specialized centers.
Conclusion. The review showed a number of deficiencies in Russian clinical guidelines. In certain documents, due attention is not paid to the provision of rehabilitation. It’s necessary to expand multidisciplinary approach in cancer patients' rehabilitation as well as the evidence base to improve Russian guidelines.
ISSN 2949-5881 (Online)