ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Objective: to determine the efficacy of comprehensive preconception care programs, including sodium chloride baths, electropulse therapy, manual therapy, and their impact on the endometrium, uterine blood flow parameters according to ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound, as well as on the pregnancy rate in patients with chronic endometritis.
Material and methods. The randomized study included 95 patients with chronic endometritis aged 28 to 45 years. In the main group, 32 women underwent a complex of electropulse therapy (10 procedures), sodium chloride baths (10 procedures), and manual therapy (5 sessions). In the comparison group, 32 patients received treatment consisting of electropulse therapy and sodium chloride baths. In 31 patients of the control group, restorative treatment was used, including electropulse therapy and fresh baths.
Results. The arterial perfusion index increased by 2.6 times (p<0.05) in the main group, and by 2.36 times (p<0.05) in the comparison group. In the control group, this parameter demonstrated no significant changes. The systolic-diastolic ratio in the right uterine artery decreased by 6.18% (p<0.001) in the control group, by 9.18% (p<0.001) in the comparison group, by 20.8% (p<0.001) in the main group. The systolic-diastolic ratio in the left uterine artery decreased by 7.44% (p<0.001) in the control group, by 9.27% (p<0.05) in the comparison group, by 20.4% (p<0.001) in the main group. The reduction in the systolic-diastolic ratio after treatment in the main group was significantly greater than that observed in the control and comparison groups (p<0.001).
Conclusion. Sodium chloride baths and manual therapy as part of comprehensive restorative treatment contribute to the improvement of endometrial structure and increase uterine blood flow volume. Manual therapy reduces vascular resistance, as evidenced by a decrease in the systolic-diastolic ratio in the uterine arteries. Electropulse therapy revealed no particular efficacy in the present study, and may be considered as part of a comprehensive therapy to enhance effects.
Background. The considerable number of surgical interventions for the treatment of discogenic lumbosacral radiculopathy
(LSR) highlights the importance of optimizing complex post-surgical rehabilitation programs, particularly those incorporating innovative physiotherapeutic techniques. One of the modern and safe methods in physiotherapeutic rehabilitation is repetitive peripheral magnetic stimulation (rPMS).
Objective: to evaluate the efficacy of a rehabilitation therapy that includes rPMS for patients with LSR during the early postoperative rehabilitation period following microdiscectomy.
Material and methods. A prospective randomized comparative study involved 71 patients with LSR following microdiscectomy. On postoperative Day 7, the patients were randomly assigned to one of two groups. Group 1 (n=35) received a course of rPMS in addition to the standard rehabilitation therapy, while Group 2 (n=36) received only the standard treatment. Pain intensity was assessed using the visual analog scale, anxiety was evaluated using the state-trait anxiety inventory, and health-related quality of life was measured with the EuroQol-5D questionnaire.
Results. On Day 21 of rehabilitation, a statistically significant difference (p=0.036) in pain intensity in the lower limb was observed between the two groups. In addition, a statistically significant difference (p=0.042) was revealed in the frequency distribution of trait anxiety severity. A statistically significant improvement in the frequency distribution of self-care level was observed in Group 1 between Days 7 and 21 (p<0.05).
Conclusion. The clinical effects observed in terms of the regression of pain, improved sensory function, and psychological wellbeing were more pronounced in the group receiving rPMS. These findings suggest that rPMS incorporated into postoperative rehabilitation programs may serve as a valuable tool for enhancing patient recovery.
Background. Providing rehabilitation care to women with external genital endometriosis (EGE) after surgical treatment requires an interdisciplinary approach to selecting patient management strategy and biomarkers for objective monitoring of health status.
Objective: to determine the feasibility of using inflammatory biomarkers in women undergoing rehabilitation after EGE surgical treatment to assess the quality of care.
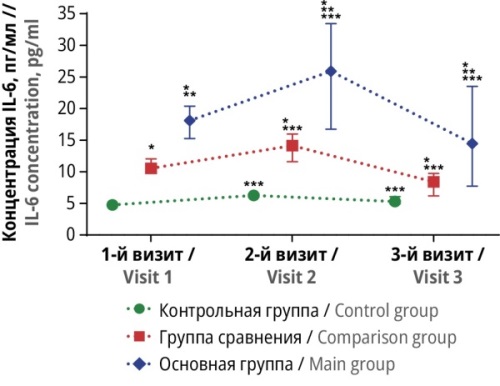
Material and methods. The study included 40 EGE patients (main group), 40 patients with other gynecological pathologies (comparison group), and 40 nearly healthy women (control group). All participants with gynecological pathologies underwent surgical treatment with subsequent rehabilitation. The severity of the inflammatory process was assessed using the following inflammation biomarkers: serum interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-a), citrullinated histone H3 (CitH3), and the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR). The dynamics of changes in biomarker levels were measured before surgery, 1 week and 3 months after it.
Results. The assessment of inflammatory biomarker serum concentrations indicated the presence of inflammatory processes in patients of both the main and comparison groups. However, the levels of IL-6, TNF-a, CitH3 and NLR among EGE patients were statistically significantly higher compared to similar parameters in women with other gynecological pathologies. One week after surgery, the main group showed a significant increase in concentrations of IL-6, CitH3 and NLR and a decrease in TNF-a levels compared to baseline values. Three months after surgery, a significant reduction in the severity of the inflammatory process in the main group was observed compared to the values obtained 1 week after surgery. In several cases, the levels of inflammatory biomarkers were statistically significantly lower than baseline values. Notably, the serum concentration of CitH3 decreased to levels observed in nearly healthy women.
Conclusion. An inflammatory process was recorded in EGE patients, which can be corrected through surgical intervention. Using serum concentrations of CitH3 as a marker for assessing the quality of surgical treatment for EGE and managing patients during the rehabilitation phase was proved to be viable.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Background. Rehabilitation services are an essential part of modern healthcare systems. Despite the achieved technological progress in medical care, gaps in the organization of effective medical rehabilitation remain unresolved.
Objective: review of current approaches to organizing effective medical rehabilitation services.
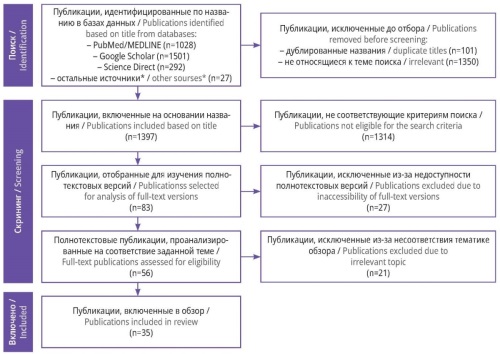
Material and methods. The search for sources published over the period of last 10 years was conducted using PubMed/ MEDLINE, Google Scholar, Science Direct, eLibrary and CyberLeninka databases. The search for documents related to the regulation of rehabilitation care was carried out using the Yandex and Google search engines. Individual references included in review articles were studied in greater detail. The selection procedure conducted in accordance with the PRISMA recommenda- tions retrieved 35 publications.
Results. The current recommendations given by World Health Organization experts were presented. The state of rehabilitation services in Russia and the experience of organizing rehabilitation services abroad were analyzed. The shortcomings of existing rehabilitation approaches were identified, along with issues related to accessibility of medical care. Gaps in legislation were indicated, and innovative technologies for solving issues with the provision of rehabilitation support were described.
Conclusion. The existing systems of providing rehabilitation services in different countries are associated with certain short- comings. In this connection, countries and research groups continue to develop schemes for optimizing the load on rehabilitation services.
The rehabilitation of neurooncology patients represents a critical issue due to the high incidence of brain tumors of varying locations and the severity of associated neurological symptoms, which significantly reduce the patient’s quality of life. Over the past decades, the prevalence of central nervous system tumor has increased by more than twofold in individuals aged 65 and above. Neurooncology patients represent a complex group that requires long-term restorative treatment. The early initiation of rehabilitation facilitates the recovery of impaired functions prior to the formation of persistent pathological patterns. This article examines neurorehabilitation methods using the example of the most common benign brain tumors, which include meningiomas, schwannomas, ependymomas, and pituitary neuroendocrine tumors. Significant advancements have been made in the treatment of these tumors in recent years, particularly through combined treatment modalities. A multidisciplinary approach to neurooncology is becoming increasingly recognized as a key element in global healthcare. However, the needs of these patients and their families extend beyond medical care, necessitating the involvement of psychologists, occupational therapists, speech-language pathologists, and social workers. A comprehensive approach to treatment, early restorative interventions and the development of innovative neurorehabilitation methods can facilitate a personalized strategy for patients with benign brain tumors, thereby increasing their rehabilitation potential.
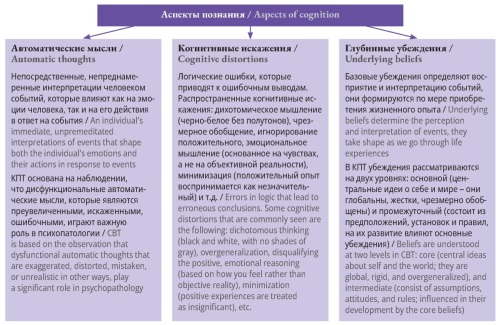
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is considered to be a highly effective and evidence-based psychotherapeutic method aimed at modifying irrational thoughts and dysfunctional behaviors. The present paper explores the theoretical foundations of CBT, its core strategies, including cognitive restructuring and behavioral activation, as well as its advantages within the framework of psychological rehabilitation. The application of CBT for rehabilitation of patients with various conditions, such as post-COVID syndrome, oncological diseases, postpartum depression, and cardiovascular disorders is analyzed. Special attention is given to the integration of digital technologies to enhance the accessibility of the therapy, including online programs and interactive modules. The role of CBT as the “gold standard” for modern psychotherapy is justified, demonstrating its high efficacy in restoring the quality of life and psycho-emotional well-being of patients.
ISSN 2949-5881 (Online)